

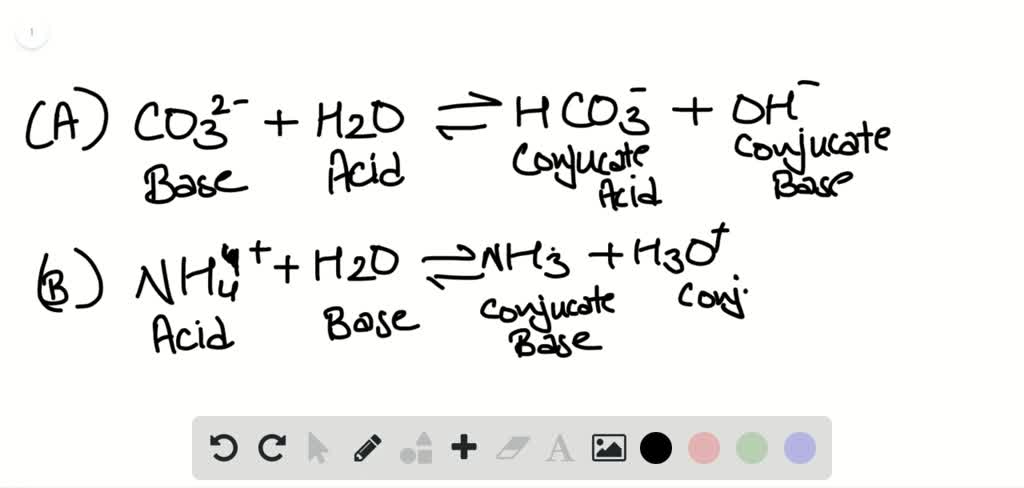


Neutralization reactions are one type of chemical reaction that proceeds even if one reactant is not in the aqueous phase. Write the neutralization reaction between H 2SO 4(aq) and Sr(OH) 2(aq). To balance this equation, we need two phosphate ions and three calcium ions we end up with six water molecules to balance the equation:ĢH 3PO 4(aq) + 3Ca(OH) 2(aq) → 6H 2O(ℓ) + Ca 3(PO 4) 2(s) According to the solubility rules, Ca 3(PO 4) 2 is insoluble, so it has an (s) phase label. The expected products are water and calcium phosphate, so the initial chemical equation is H 3PO 4(aq) + Ca(OH) 2(aq) → H 2O(ℓ) + Ca 3(PO 4) 2(s).To balance the equation, we need to realize that there will be two H 2O molecules, so two HNO 3 molecules are required:ĢHNO 3(aq) + Ba(OH) 2(aq) → 2H 2O(ℓ) + Ba(NO 3) 2(aq) The expected products are water and barium nitrate, so the initial chemical reaction is HNO 3(aq) + Ba(OH) 2(aq) → H 2O(ℓ) + Ba(NO 3) 2(aq).Write the neutralization reactions between each acid and base.įirst, we will write the chemical equation with the formulas of the reactants and the expected products then we will balance the equation. (This is one of several reactions that take place when a type of antacid-a base-is used to treat stomach acid.) However, in the reaction between HCl(aq) and Mg(OH) 2(aq), additional molecules of HCl and H 2O are required to balance the chemical equation:ĢHCl(aq) + Mg(OH) 2(aq) → 2H 2O(ℓ) + MgCl 2(aq) By counting the number of atoms of each element, we find that only one water molecule is formed as a product. (In chemistry, the word salt refers to more than just table salt.) For example, the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between HCl(aq) and KOH(aq) is Where the term salt is generally used to define any ionic compound (soluble or insoluble) that is formed from a reaction between an acid and a base. In fact, the general reaction between an acid and a base is Although acids and bases have their own unique chemistries, the acid and base cancel each other’s chemistry to produce a rather innocuous substance-water. The reaction of an acid and a base is called a neutralization reaction. We use the hydronium ion as the more logical way a hydrogen ion appears in an aqueous solution, although in many chemical reactions H + and H 3O + are treated equivalently. To represent this chemically, we define the hydronium ion H 3O +(aq), a water molecule with an extra hydrogen ion attached to it, as H 3O +, which represents an additional proton attached to a water molecule. What is more likely is that the H + ion has attached itself to one (or more) water molecule(s). Do we really have bare protons moving about in aqueous solution? No. You may recognize that, based on the description of a hydrogen atom, an H + ion is a hydrogen atom that has lost its lone electron that is, H + is simply a proton. These original definitions were proposed by Arrhenius (the same person who proposed ion dissociation) in 1884, so they are referred to as the Arrhenius definitions of an acid and a base, respectively. The equivalent definition of a base is that a base is a compound that increases the amount of hydroxide ion (OH −) in an aqueous solution. The chemical opposite of an acid is a base. Now we can redefine an acid: an acid is any compound that increases the amount of hydrogen ion (H +) in an aqueous solution. This is slightly incorrect, but until additional concepts were developed, a better definition needed to wait. In the section called “Acids”, we defined an acid as an ionic compound that contains H + as the cation. Identify a neutralization reaction and predict its products.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
